Introduction to GitHub and Version Control
🙋Hi! I am Ondřej Mottl
Assistant Professor at Charles University
Head of 🧑💻Laboratory of Quantitative Ecology
- 📧 Ondrej.mottl(at)gmail.com
- 🦋 ondrejmottl.bsky.social
- 🐱 Github OndrejMottl
- 🆔 ORCID 0000-0002-9796-5081
- 🌐 bit.ly/ondrej_mottl

This presentation
😸Code on GitHub: OndrejMottl/VersionControl_FZU_November2025
🖼️Slides: bit.ly/mottl_prez_fzu_202511
What we’ll cover today
🎯 Main Topics
- What is version control?
- Technical setup
- Make a record of a change (commit)
- Sync changes with remote server
- Collaboration through branches
- Pull Requests workflow
✅ By the end, you’ll be able to:
- Understand basic git terminology
- Create a GitHub repo
- Make commits and push/pull changes
- Handle merge conflicts
- Work with branches and Pull Requests
Evolution

Open Science

A better view

The Journey

Version control
Ring a bell?
What is Version Control? 🤔

It is all about keeping track of changes 📓✍️
Exercise
03:00 Do you recognize some of these questions?
- It broke … hopefully I have a working version somewhere?
- Can you please send me the latest version?
- Which version are you using?
- I am sure it used to work. When did it change?
- My laptop is gone. Is my data now gone?
Fundamentals
Project self-containment

Each “paper” is a single project.
Project file structure

Git
- local software
- keep track of changes of files

GitHub
- host server
- store (git) the data
- project management, collaboration, publishing

Git/GitHub setup AKA “git hell”

Follow instructions in Version Control - git hell (a separate presentation).
Getting all the necessary software installed, configured, and playing nicely together is honestly half the battle … Brace yourself for some pain
Weapon of choice (GUI)
GUI = Graphical User Interface
I will be showing you how to use:
You still can use the shell.
Basic vocabulary
- A script is a record of code.
- Project is self contained project/study/paper containg scripts, data, figures, etc.
- Every such project is called repository (ie a repo)
- Your local repository is called local
- Your online repository, is called remote
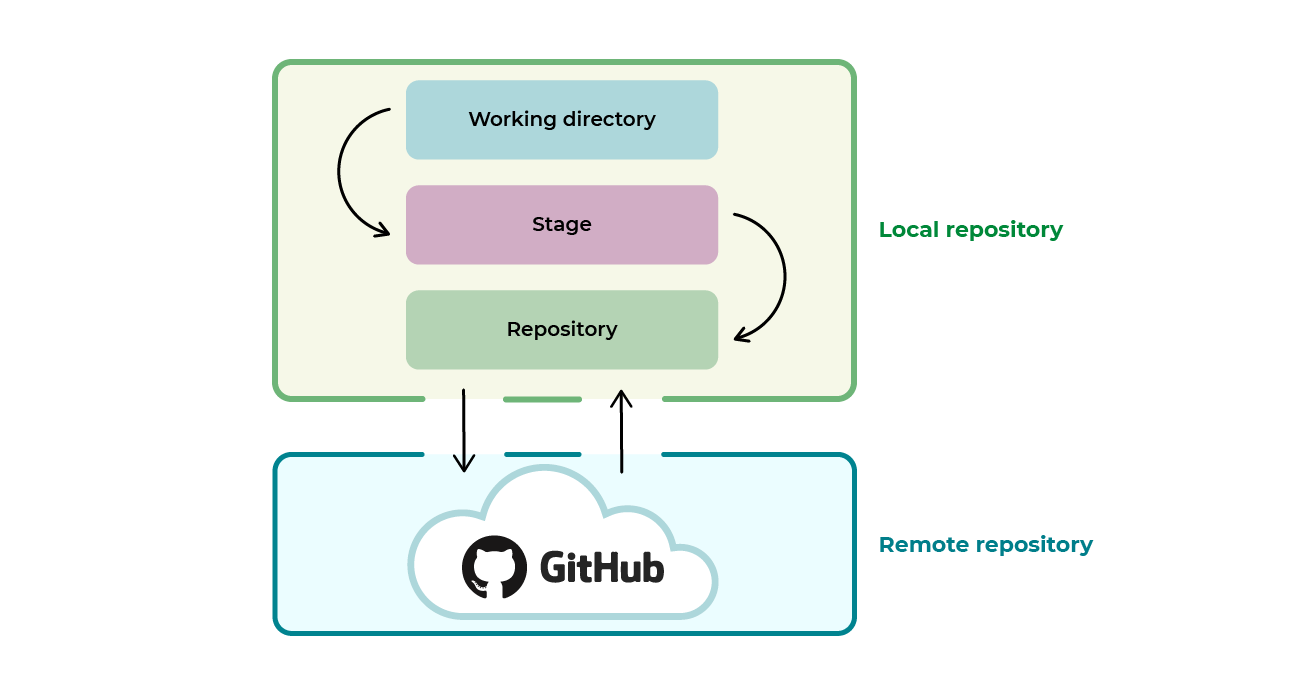
Note on practical exercises

Git init (project first)
Activate git for a repo
Practical Exercise
- Make a new project with Git tracking
05:00 A record of a change
a commit
A commit is a record of a change
If you create or edit a file in your repository and save the changes, you need to record your change via a commit
Chess analogy?

Chess move diary:
- Bc4 (Bishop to c4)
- Nf3 (Knight to f3)
- Qc7 (Queen to c7)
a commit

Pawn to d4

Edit line 32 of file A
a commit

3 states of a file
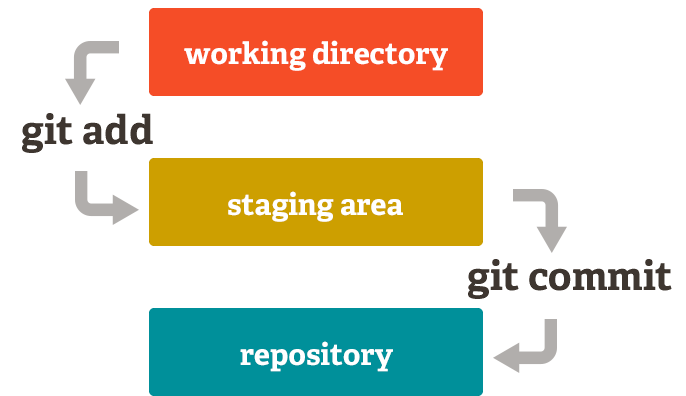

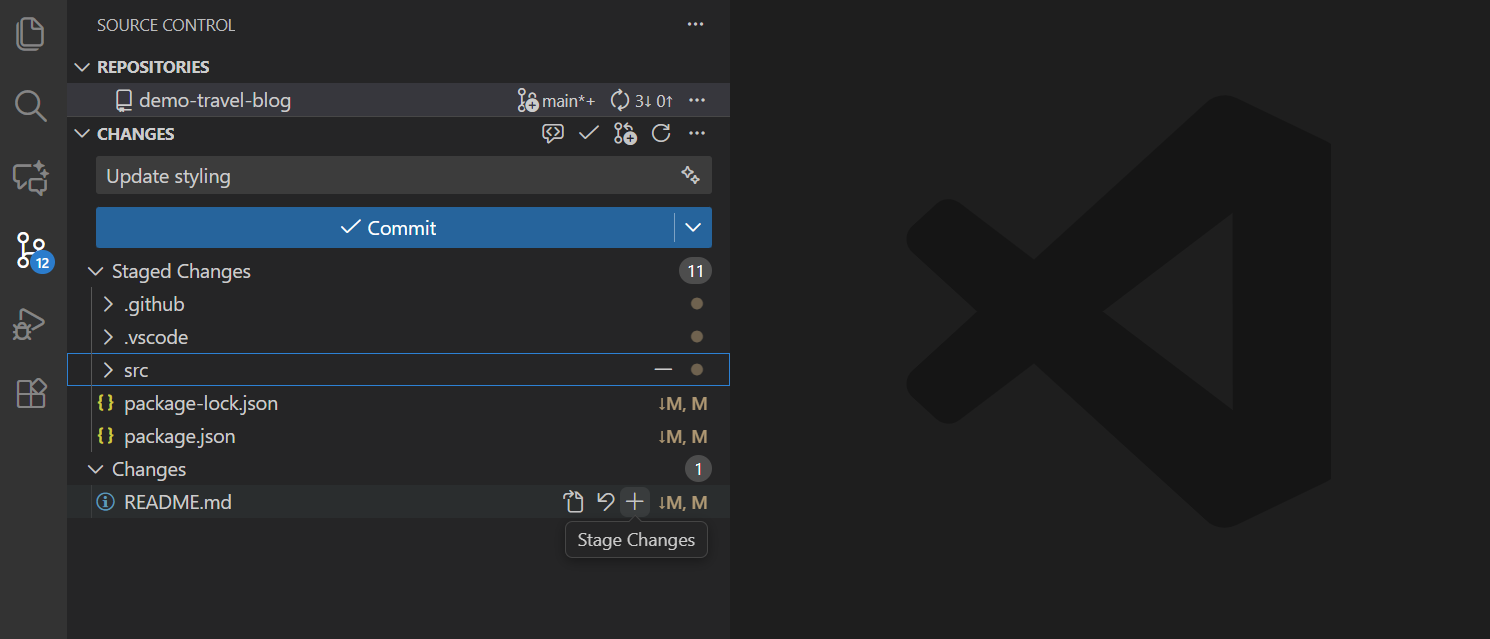
Staging changes
Make a change to a file and save it. Now stage the change:
Practical Exercise
- Make changes to (a) file(s)
- Make a new file
- Stage and Unstage the changes
05:00 a first commit
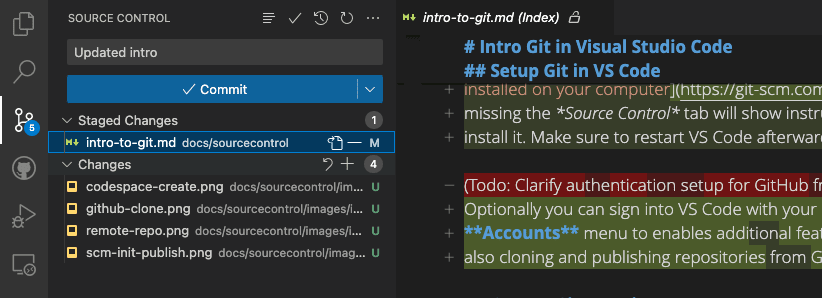
Commit (record) staged changes:
Review history
$ git log --stat
commit 085bb3bcb608e1e8451d4b2432f8ecbe6306e7e7
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 16:40:33 2008 -0700
Remove unnecessary test
lib/simplegit.rb | 5 -----
1 file changed, 5 deletions(-)
commit a11bef06a3f659402fe7563abf99ad00de2209e6
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 10:31:28 2008 -0700
Initial commit
README | 6 ++++++
Rakefile | 23 +++++++++++++++++++++++
lib/simplegit.rb | 25 +++++++++++++++++++++++++
3 files changed, 54 insertions(+)Dissecting a commit
SHA - unique identifier
Author - who has done this?
Date - when was this done?
Message - description of what has been done
Stats - what has changed?
Practical Exercise
- commit some changes
- review history
05:00 Commit message
Commits are quick and cheap. Therefore:
- commit often (!)
- provide useful commit messages.

Commit history
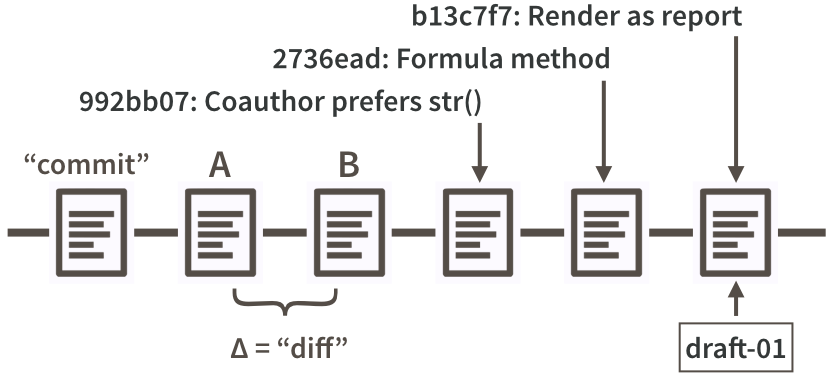
Remote
remote
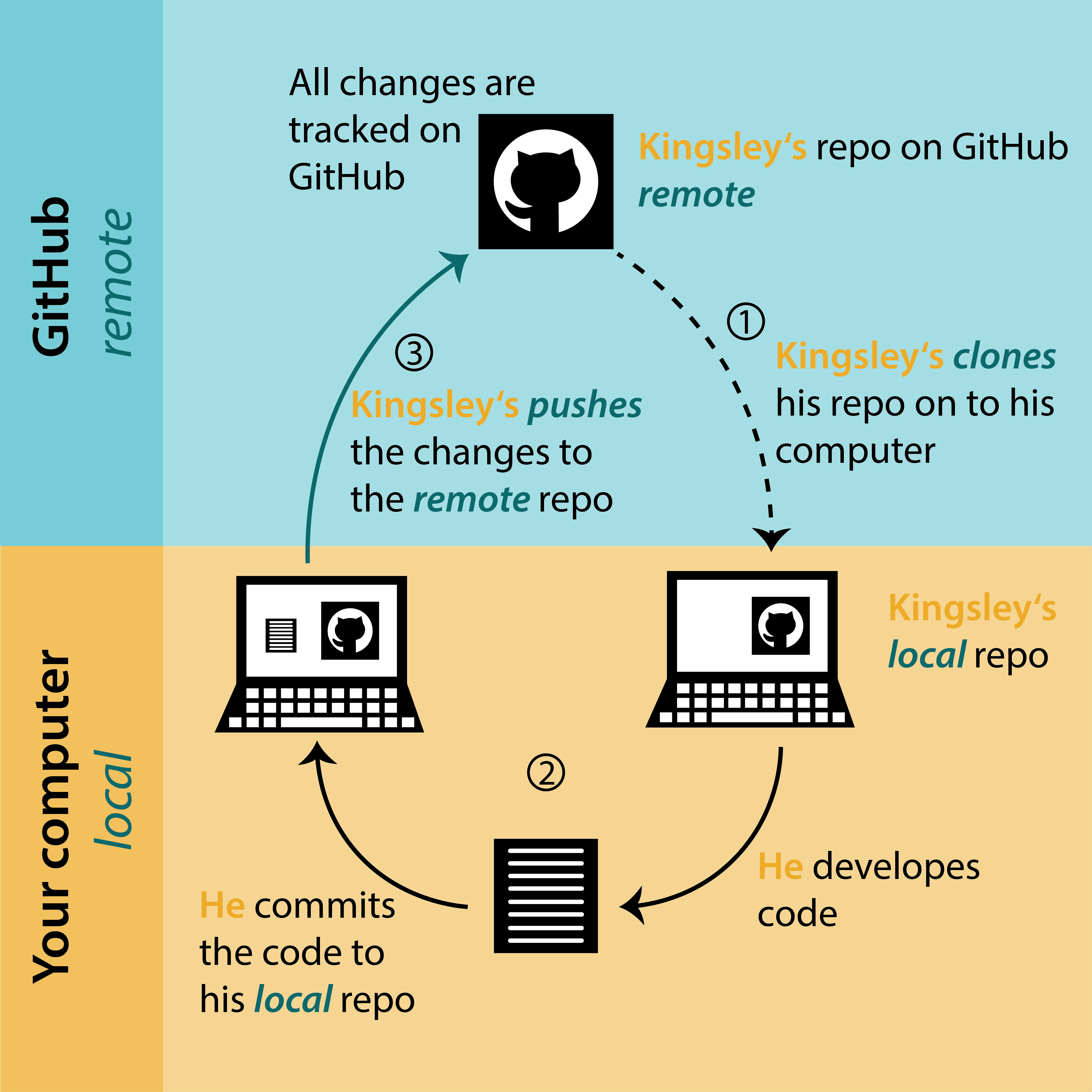
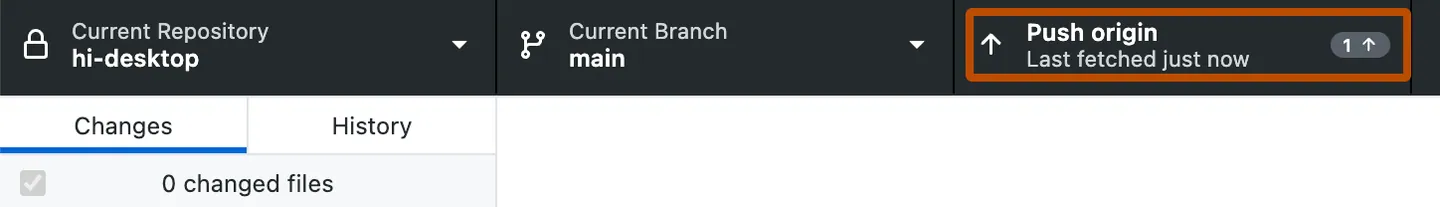
Update remote - PUSH
Now we need to sync changes with the remote using PUSH
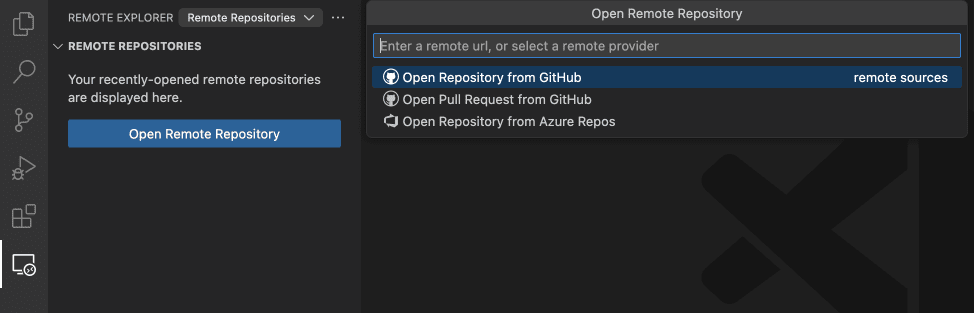
Add a remote to existing local repo (only once):
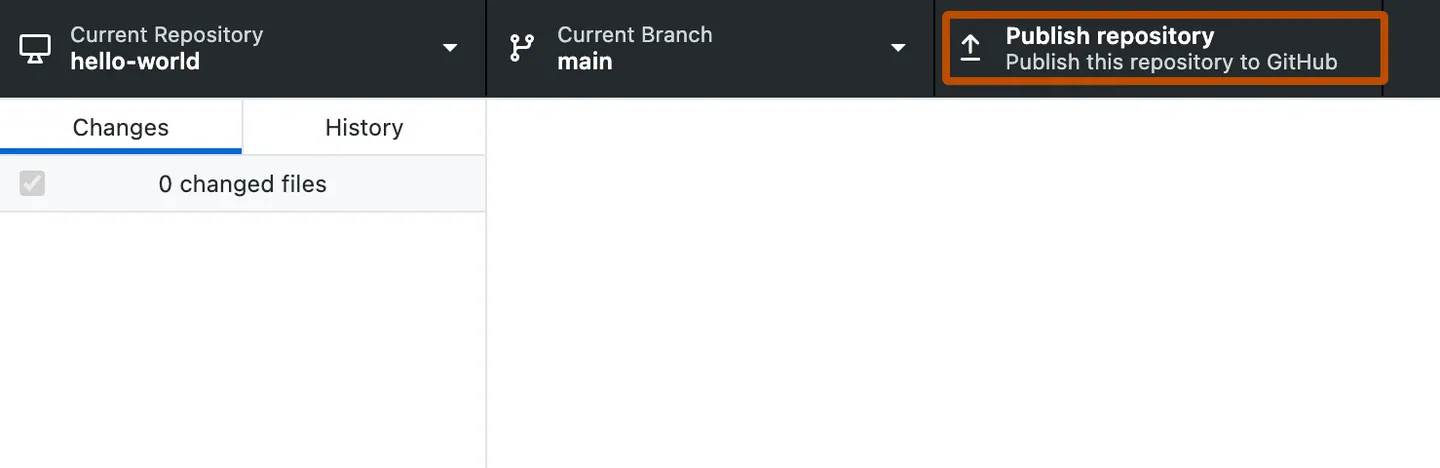
Push local to remote (GitHub):
Add a remote to existing local repo (only once):
Push local to remote (GitHub):
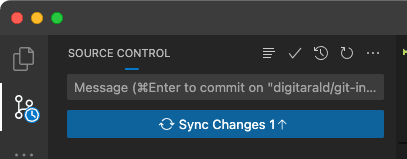
Practical Exercise
- Publish repo to GitHub
- make new commit(s)
- Push changes to remote
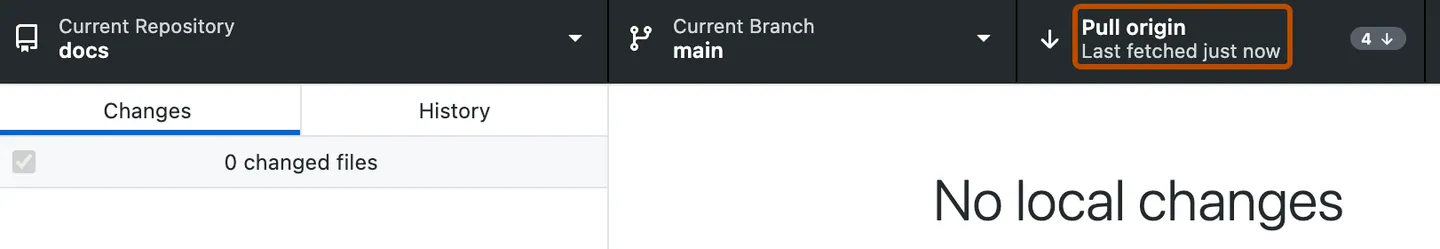
05:00 update local- PULL

update local- PULL
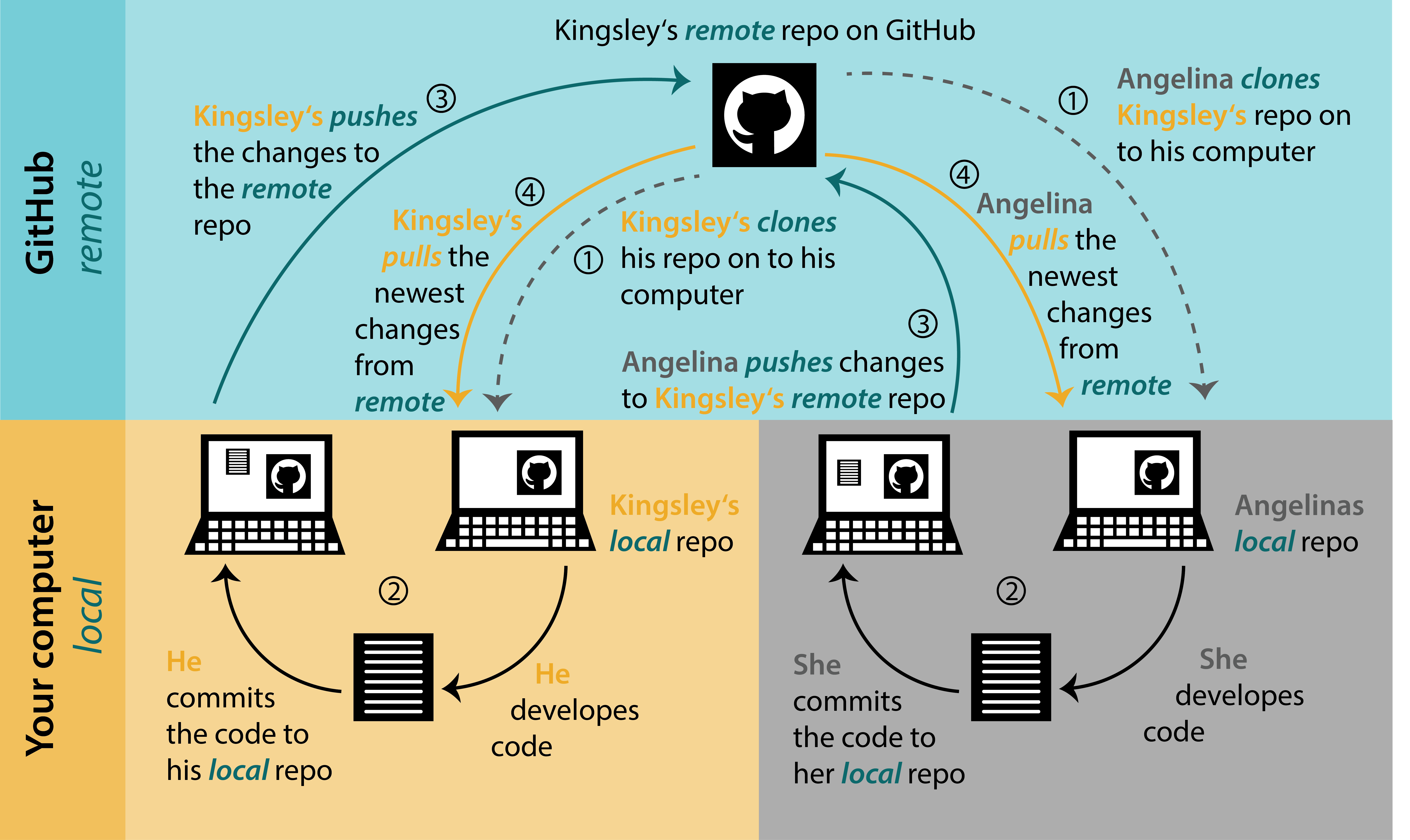
update local- PULL
Now we need to sync changes from the remote to local using PULL
GitHub intermezzo
A GitHub repo
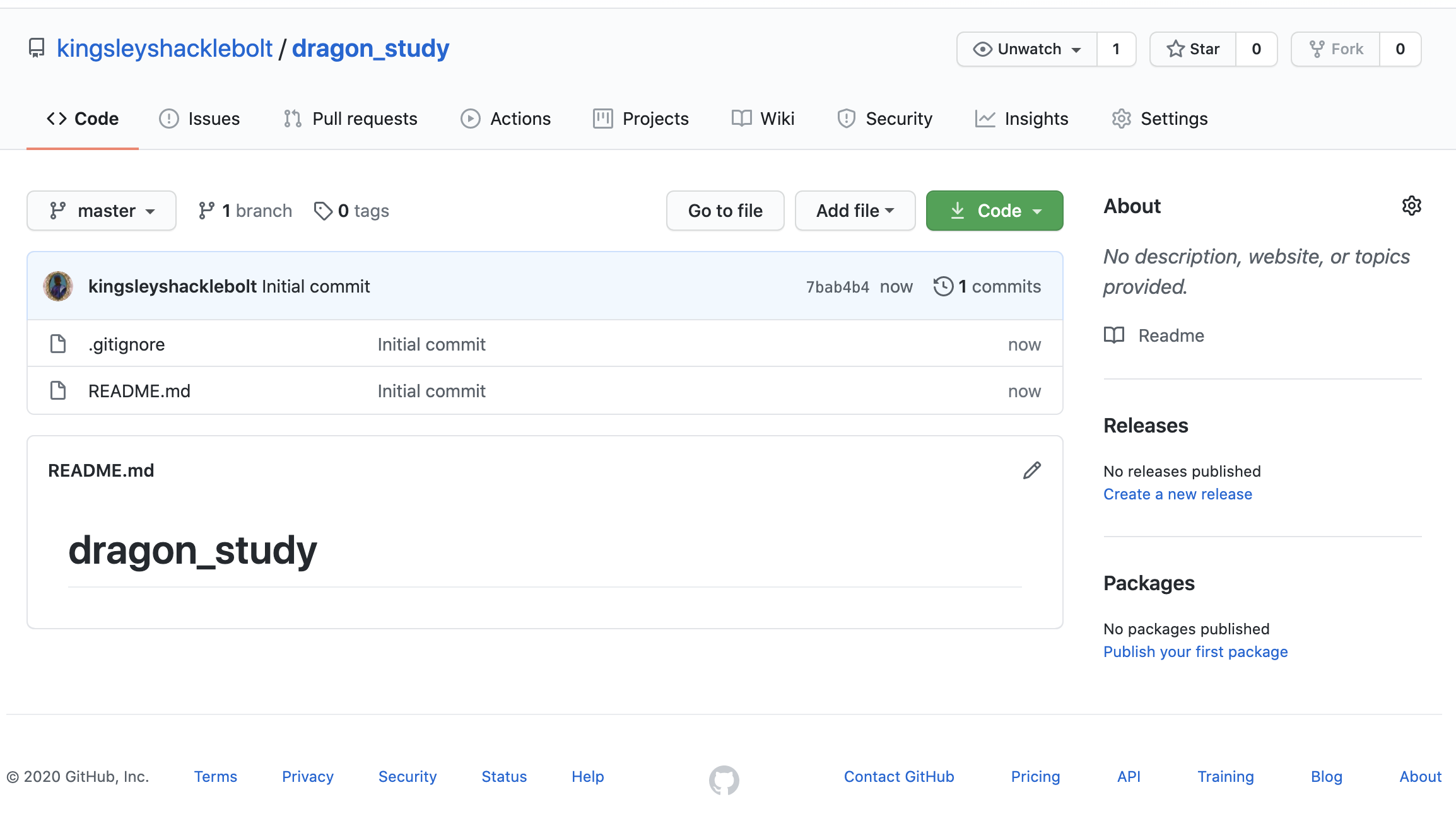
GitHub creating a repo (repo first)

GitHub creating a repo (repo first)

GitHub creating a repo (repo first)

GitHub creating a repo (repo first)

GitHub creating a repo (repo first)
README - description of the project
.gitignore - list of files ignored by GitHub (more about it later)
license - tell other what they can do with your code

GitHub creating a repo (repo first)

Practical Exercise
- Create a new repo on GitHub
- Delete a repo on GitHub
05:00 Sharing your repo
Github allows you to specify roles and permissions of your repo.

Roles (permissions)

Practical Exercise
- Add someone as a collaborator to your repo
- Change the role of the collaborator
- Remove the collaborator
05:00 Git Clone (repo first)

Git clone (repo first)
Copy (download) from remote repo to local machine
Example of online repo: OndrejMottl/VersionControl-playground
Practical Exercise
- clone a repo (e.g. any repo from OndrejMottl)
05:00 Merge conflict
Merge conflict 💩💩💩
A merge conflict can occur when you are changing the same line in one file differently.
Merge conflict 💩💩💩
To https://github.com/picardis/myrepo.git
! [rejected] master -> master (fetch first)
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://github.com/picardis/myrepo.git'
hint: Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do
hint: not have locally. This is usually caused by another repository pushing
hint: to the same ref. You may want to first integrate the remote changes
hint: (e.g., 'git pull ...') before pushing again.
hint: See the 'Note about fast-forwards' in 'git push --help' for details.a good strategy to avoid such conflicts:
- Commit often
- Work in small steps
- Push and pull regularly
- Organize your code in small modules (scripts)
Merge conflicts cannot always be avoided (but can be mitigated by branches; later).
Merge conflict 💩💩💩
Ups! I have made a mistake 😮
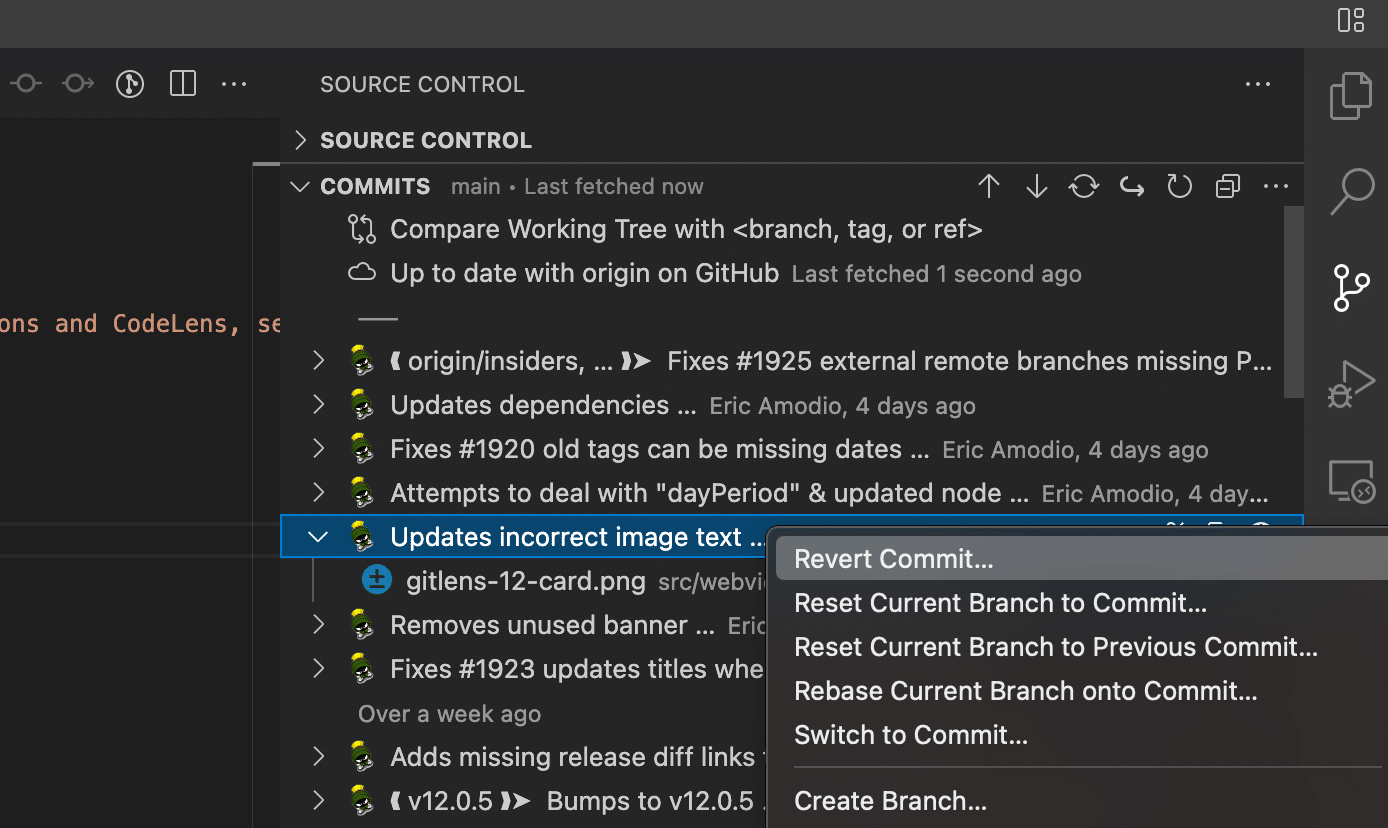
How to undo last commit?
Variant A: I commited but NOT pushed yet.
Ups! I have made a mistake 😮
How to undo last commit?
Variant B: I commited AND pushed already.
Branches
Branches
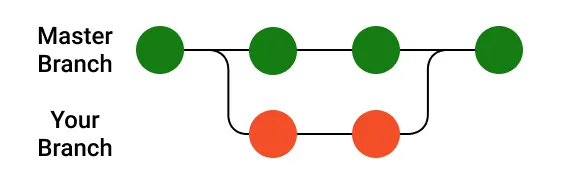
Branches

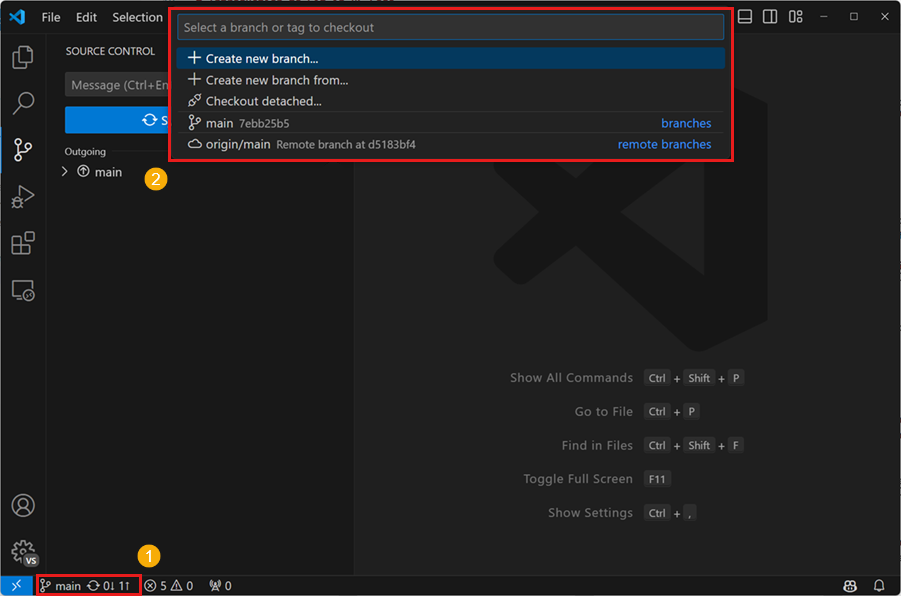
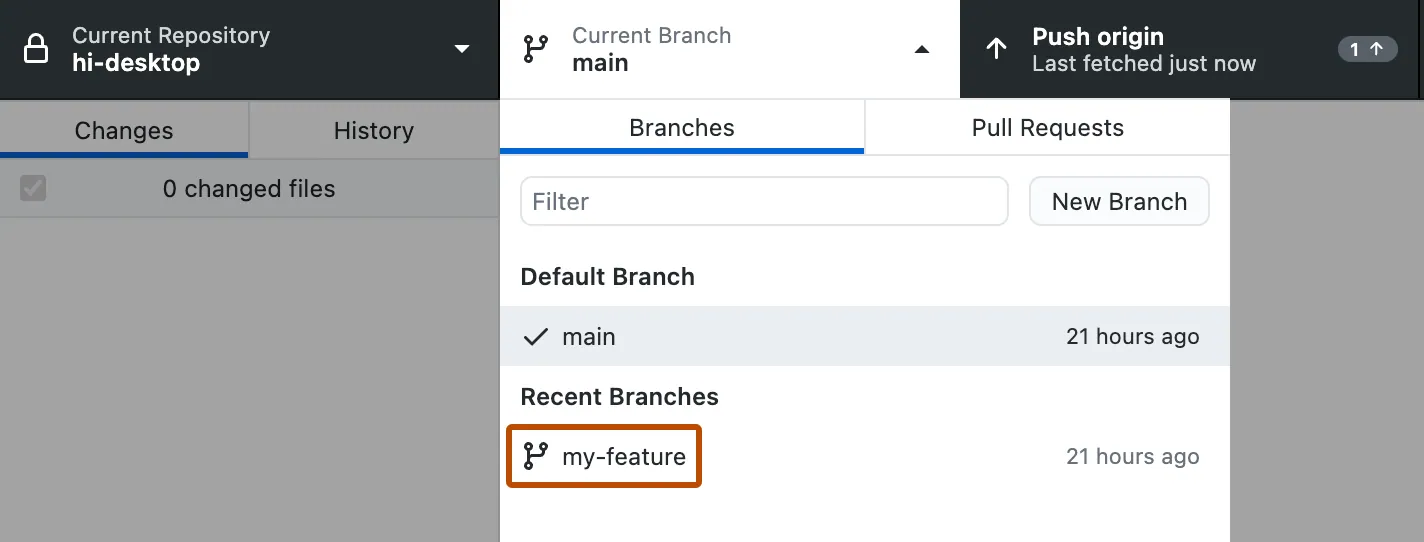
Make a branch
Switching between branches
The default branch is called main or master
Switching between branches is sometimes called (checkout)
‼️ Make sure that you have all changes commited before switching ‼️
Practical Exercise
- Make a branch and switch
- commit changes
- push to remote
05:00 Merging branches

Merging branches
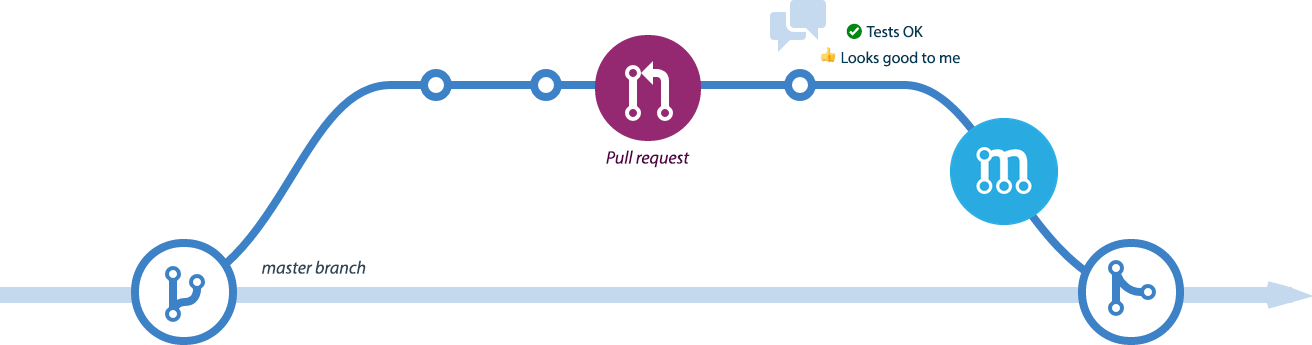
Pull Request (PR)
Request to merge a branch

Pull Request - create
After you push new branch, you should have a green button Compare & pull request on GitHub
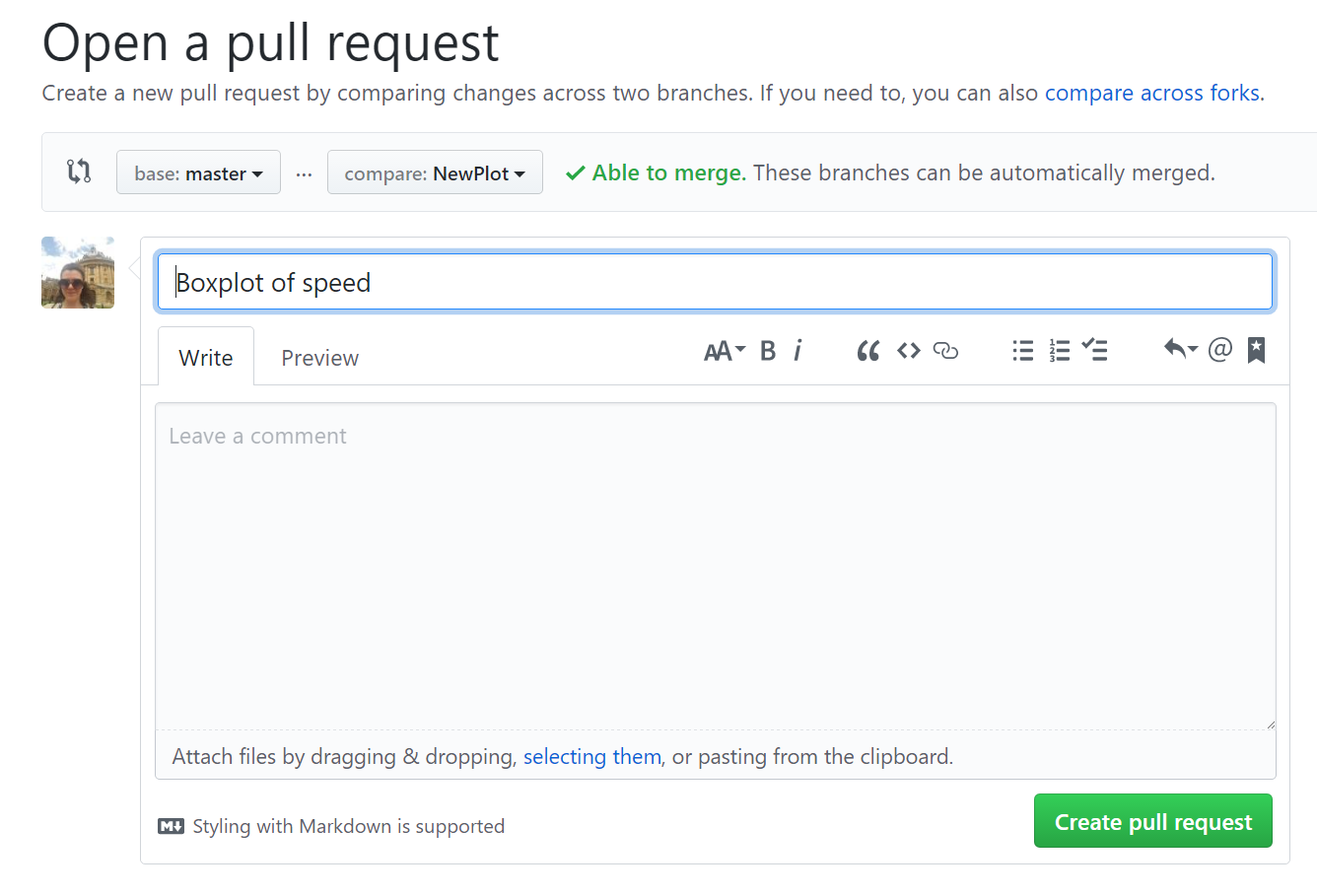
Pull Request - components
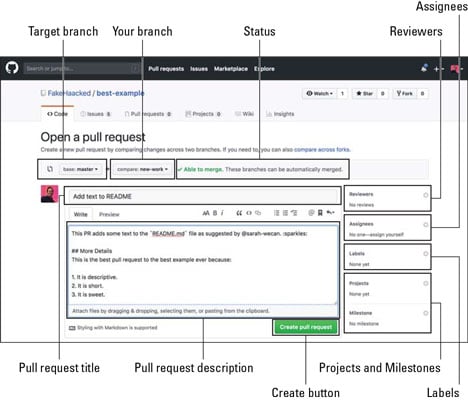
Pull Request - Overview
Now you can add more commits on GitHub, (add Comment to start discussion), or merge the branch.
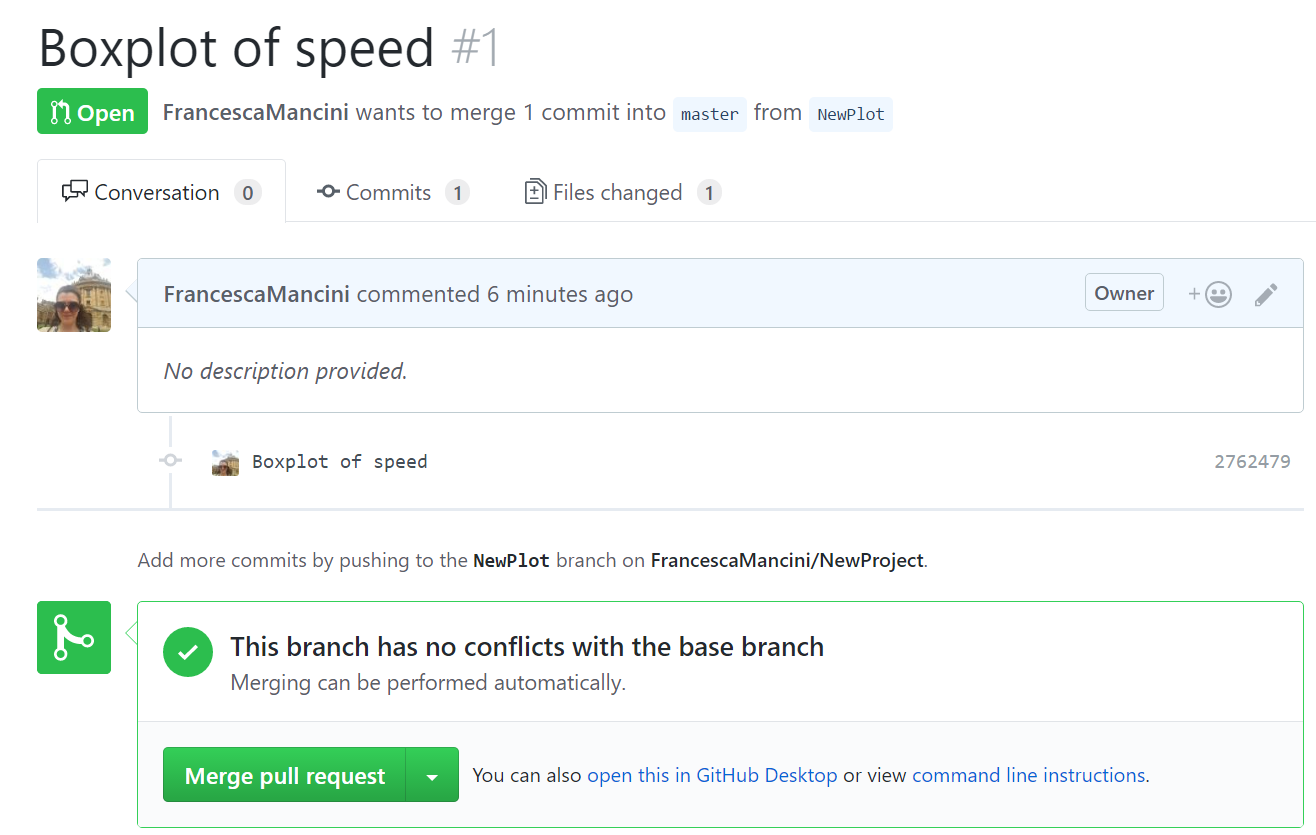
Practical Exercise
- Create a PR
25:00 Note on Markdown
You can use Markdown on GitHub in the description and comments
More details on Github Docs

Pull Request - review
A tool to review on GitHub suggested changes

Collaboration

Pull Request - review
On someone else’s PR on GitHub, you can comment on individual lines or whole files

Pull Request - review

Merging branches
Merge conflict with branch 💩
Merge conflict with branches is much more pleasant😎

Merge conflict with branch 💩
Edit the file as needed

Merge conflict with branch 💩
Commit the changes

Practical Exercise
- Merge a branch
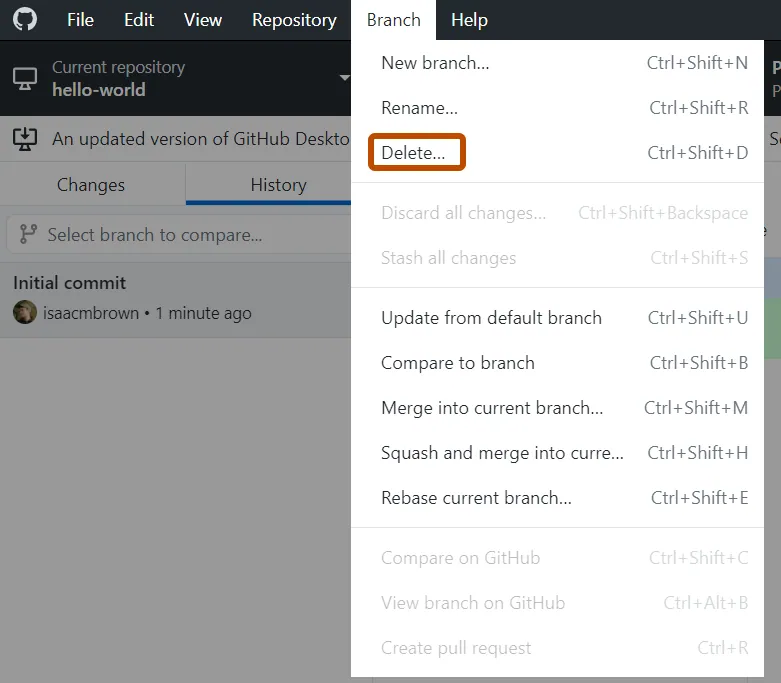
05:00 Delete branch
We can delete branch directly on GitHub after merging
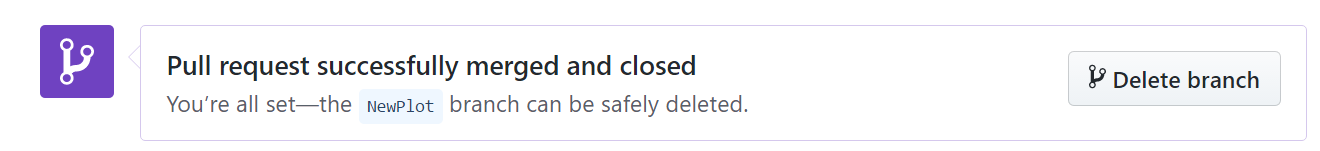
Delete branch
We can also delete branch before merging
Practical Exercise
- Delete a branch
05:00 Outro
GitHub tools suite


Introduction to GitHub and Version Control
28.11.2025